Solubility Of 1-butanol In Water
Butanol (likewise called butyl alcohol) is a four-carbon alcohol with a formula of C4HnineOH, which occurs in five isomeric structures (4 structural isomers), from a straight-concatenation master alcohol to a branched-chain third alcohol;[i] all are a butyl or isobutyl group linked to a hydroxyl grouping (sometimes represented as BuOH, n-BuOH, i-BuOH, and t-BuOH). These are due north-butanol, 2 stereoisomers of sec-butanol, isobutanol and tert-butanol. Butanol is primarily used as a solvent and as an intermediate in chemical synthesis, and may be used as a fuel. Biologically produced butanol is called biobutanol, which may be northward-butanol or isobutanol.
Isomers [edit]
The unmodified term butanol unremarkably refers to the straight chain isomer with the alcohol functional grouping at the terminal carbon, which is besides known as n-butanol or 1-butanol. The straight chain isomer with the booze at an internal carbon is sec-butanol or two-butanol. The branched isomer with the alcohol at a last carbon is isobutanol or 2-methyl-1-propanol, and the branched isomer with the booze at the internal carbon is tert-butanol or ii-methyl-2-propanol.
The butanol isomers have different melting and boiling points. n-butanol and isobutanol have limited solubility, sec-butanol has essentially greater solubility, while tert-butanol is miscible with h2o. The hydroxyl group makes the molecule polar, promoting solubility in water, while the longer hydrocarbon concatenation mitigates the polarity and reduces solubility.
Toxicity [edit]
Butanol exhibits a low club of toxicity in unmarried dose experiments with laboratory animals [2] [3] and is considered safe enough for apply in cosmetics. Brief, repeated overexposure with the skin tin effect in depression of the key nervous system, as with other short-chain alcohols. Exposure may also cause astringent eye irritation and moderate skin irritation. The primary dangers are from prolonged exposure to the alcohol's vapors. In extreme cases this includes suppression of the key nervous system and fifty-fifty death. Under about circumstances, butanol is apace metabolized to carbon dioxide. It has non been shown to damage Deoxyribonucleic acid or cause cancer.
Uses [edit]
Primary uses [edit]
Butanol is used as a solvent for a broad variety of chemical and fabric processes, in organic synthesis, and as a chemical intermediate. It is also used every bit a paint thinner and a solvent in other coating applications where a relatively deadening evaporating latent solvent is preferable, equally with lacquers and ambience-cured enamels. It is also used as a component of hydraulic and brake fluids.[4]
A 50% solution of butanol in water has been used since the 20th century to retard the drying of fresh plaster in fresco painting. The solution is usually sprayed on the wet plaster after the plaster has been trowelled smooth and extends the working period during which frescos can be painted upwards to 18 hours.[5]
Butanol is used in the synthesis of two-butoxyethanol. A major application for butanol is as a reactant with acrylic acid to produce butyl acrylate, a primary ingredient of water based acrylic paint.[6]
It is also used as a base for perfumes, but on its ain has a highly alcoholic olfactory property.
Salts of butanol are chemical intermediates; for example, alkali metal salts of tert-butanol are tert-butoxides.
Recreational Apply [edit]
Butanol is a primal nervous organization depressant. It can have effects similar to ethanol when ingested or drunkard past living beings such every bit humans.[ citation needed ]
Biobutanol [edit]
Butanol (due north-butanol or isobutanol) is a potential biofuel (butanol fuel).[7] Butanol at 85 percentage concentration tin be used in cars designed for gasoline (petrol) without any alter to the engine (unlike 85% ethanol), and it contains more than energy for a given book than ethanol and almost every bit much as gasoline, and a vehicle using butanol would return fuel consumption more comparable to gasoline than ethanol. Butanol can too be added to diesel fuel to reduce soot emissions.[viii] Photoautotrophic microorganisms, like cyanobacteria, can be engineered to produce 1-butanol indirectly from CO2 and water.[9]
Production [edit]
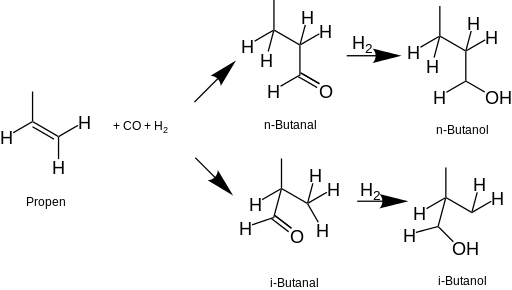
Since the 1950s, most butanol in the United States is produced commercially from fossil fuels. The nigh common process starts with propene (propylene), which is put through a hydroformylation reaction to form butanal, which is then reduced with hydrogen to 1-butanol and/or 2-butanol. tert-butanol is derived from isobutane as a co-product of propylene oxide production.
Butanol tin also be produced by fermentation of biomass by bacteria. Prior to the 1950s, Clostridium acetobutylicum was used in industrial fermentation to produce n-butanol.
See also [edit]
- A.B.Due east. procedure
- Algal fuel
- Butanol fuel
- Solvent
References [edit]
- Merck Alphabetize, twelfth Edition, 1575.
- ^ Atsumi, S.; Hanai, T.; Liao, J. C. (2008). "Non-fermentative pathways for synthesis of branched-chain college alcohols equally biofuels". Nature. 451 (7174): 86–9. doi:ten.1038/nature06450. PMID 18172501.
- ^ sixteen ECETOC JACC No. 41 n-Butanol (CAS No. 71-36-3), European Eye for Ecotoxicology and Toxicology of Chemicals, Brussels, December 2003, pages 3-4.
- ^ "north-Butanol". Archived from the original on 2015-04-02. Retrieved 2012-02-03 .
- ^ Isobutanol at chemicalland21.com
- ^ "diego's assistants | Diego Rivera Mural Project". www.riveramural.org . Retrieved 2019-03-27 .
- ^ Harris O.; et al. (August 1998). Toxicological Contour for 2-Butoxyethanol and 2-butoxyethanol acetate. U.S. Dept of Wellness and Human being Services.
- ^ Sampa Maiti; et al. (December 10, 2015). "Quest for sustainable bio‐production and recovery of butanol as a promising solution to fossil fuel". Free energy Research. doi:10.1002/er.3458.
- ^ Antoni, D.; Zverlov, V. & Schwarz, W. H. (2007). "Biofuels from Microbes". Practical Microbiology and Biotechnology. 77: 23–35. doi:10.1007/s00253-007-1163-x. PMID 17891391.
- ^ Liu, X., Miao, R., Lindberg, P., & Lindblad, P. (2019). Modular engineering for efficient photosynthetic biosynthesis of one-butanol from CO 2 in cyanobacteria. Free energy & Environmental Science, 12(9), 2765-2777.
Solubility Of 1-butanol In Water,
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Butanol
Posted by: hansenlize1938.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Solubility Of 1-butanol In Water"
Post a Comment